Introduction to Android WorkManager
03 Feb 2019Introduction
Every Android app has a main thread which is in charge of handling UI (including measuring and drawing views), coordinating user interactions, and receiving lifecycle events. If there is too much work happening on this thread, the app appears to hang or slow down, leading to an undesirable user experience. Any long-running computations and operations such as decoding a bitmap, accessing the disk, or performing network requests should be done on a separate background thread.
Applications may also require some tasks to run even when the user is not actively using the app such as syncing periodically with a backend server or fetching new content within an app on a periodic basis. Applications may also require services to run immediately to completion even after the user has completed interacting with the app. Google created a guide called Guide to background processing which determines which solution best meets your needs for these use cases.
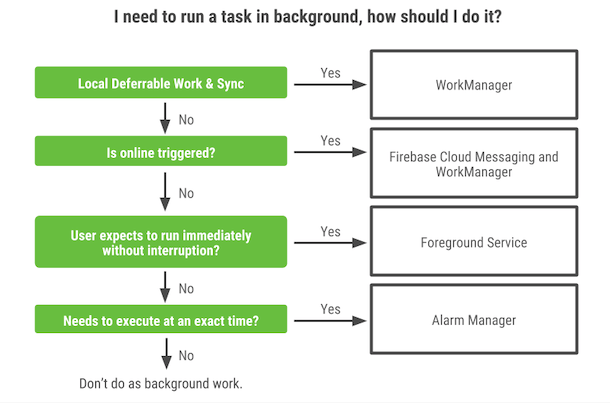
Diagram from Modern background execution in Android
WorkManager
Title WorkManager is part of Android Jetpack and an Architecture Component for background work that needs a combination of opportunistic and guaranteed execution. Opportunistic execution means that WorkManager will do your background work as soon as it can. Guaranteed execution means that WorkManager will take care of the logic to start your work under a variety of situations, even if you navigate away from your app.
WorkManager is a simple, but incredibly flexible library that has many additional benefits. These include:
- Support for both asynchronous one-off and periodic tasks
- Support for constraints such as network conditions, storage space, and charging status
- Chaining of complex work requests, including running work in parallel
- Output from one work request used as input for the next
- Handles API level compatibility back to API level 14(see note)
- Works with or without Google Play services
- Follows system health best practices
- LiveData support to easily display work request state in UI
Get started
Add the WorkManager dependency in Java or Kotlin to your Android project by openning the build.gradle file for your project and add the google() repository as shown below:
allprojects { repositories { google() jcenter() } }
Add the dependencies for the artifacts you need in the build.gradle file for your app or module. Currently you are able to add AndroidX dependencies or legacy Pre-AndroidX dependencies, so please choose the dependence what fit your project. Remember you can also add the $work_version into your gradle.build (project scope).
dependencies { def work_version = "2.0.1" // (Java only) implementation "androidx.work:work-runtime:$work_version" // Kotlin + coroutines implementation "androidx.work:work-runtime-ktx:$work_version" // optional - RxJava2 support implementation "androidx.work:work-rxjava2:$work_version" // optional - Test helpers androidTestImplementation "androidx.work:work-testing:$work_version" }
By default, WorkManager is initialized using a ContentProvider with a default Configuration. ContentProviders are created and run before the Application object, so this allows the WorkManager singleton to be setup before your code can run in most cases. This is suitable for most developers. However, you can provide a custom Configuration by using Configuration.Provider or initialize(android.content.Context, androidx.work.Configuration).
WorkManager BroadcastReceivers to monitor Constraints on devices before API 23. The BroadcastReceivers are disabled on API 23 and up. In particular, WorkManager listens to the following Intents:
android.intent.action.ACTION_POWER_CONNECTED
android.intent.action.ACTION_POWER_DISCONNECTED
android.intent.action.BATTERY_OKAY
android.intent.action.BATTERY_LOW
android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_LOW
android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_OK
android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE
In addition, WorkManager listens to system time changes and reboots to properly reschedule work in certain situations. For this, it listens to the following Intents:
android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED
android.intent.action.TIME_SET
android.intent.action.TIMEZONE_CHANGED
WorkManager uses the following permissions:
android.permission.WAKE_LOCK to make //it can keep the device awake to complete work before API 23
android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE //to listen to network changes before API 23 and monitor network Constraints
android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED //to listen to reboots and reschedule work properly.
Note that WorkManager may enable or disable some of its BroadcastReceivers at runtime as needed. This has the side-effect of the system sending ACTION_PACKAGE_CHANGED broadcasts to your app. Please be aware of this use case and architect your app appropriately.
